An Investigation of the Adoption of Net-Zero Buildings (NZBs) in the South African Commercial Property Market
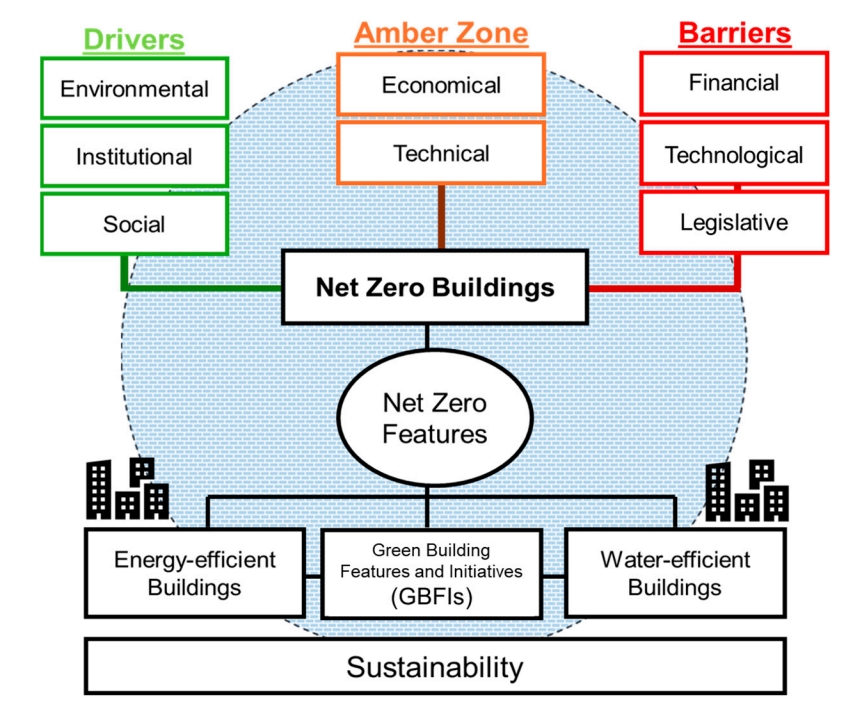
This study investigates factors influencing net-zero building (NZB) adoption in the South African commercial property sector through a qualitative analysis of four case studies, with a net-zero carbon building focus. Findings indicate that while green building certifications have exceeded 1000 since 2009, NZB adoption remains limited (64 certifications as of 2024). Key barriers include retrofit cost premiums (20–30%), technical capacity gaps, and insufficient policy frameworks. Primary drivers comprise demonstrated energy efficiency gains (15–25% reductions), tenant demand for sustainable properties, and institutional support through certification programs. This research contributes an empirical model identifying transitional “Amber Zone” factors, including energy security concerns and renewable energy returns on investment, which mediate between barriers and drivers. Case evidence shows NZB implementation can be achieved within existing budgets through integrated design approaches. These findings provide a structured framework for understanding NZB adoption dynamics in emerging markets facing similar energy and sustainability challenges.
Abstract based directly on original source.


Comments