Transformative Innovation Policy (TIP) for Human Settlements in South Africa
An explanatory index page of TIP resources available on uKESA
28 November 2025
Mark Napier
English
Information page
Council for Scientific and Industrial Research
Africa
Context and Rationale
South Africa’s human settlements sector faces systemic challenges rooted in historical spatial inequality, rapid urbanisation, and insufficient delivery capacity. Despite progress since 1994, settlements remain spatially fragmented with low densities and long commuting distances, marked by unequal access to services and opportunities, burdened by a housing backlog, and vulnerable to climate-related hazards such as flooding and heat stress. Municipalities continue to struggle with financial constraints, limited technical capacity, and ageing infrastructure, while weak coordination and the slow adoption of innovative approaches further hinder transformation. Traditional housing delivery models and incremental improvements cannot resolve these systemic problems. Transformative Innovation Policy (TIP) provides a valuable lens for reimagining South Africa’s human settlements.
This information page synthesises key insights from leading research and case studies to guide policymakers, researchers, and practitioners in shaping innovation policies that deliver transformative outcomes.
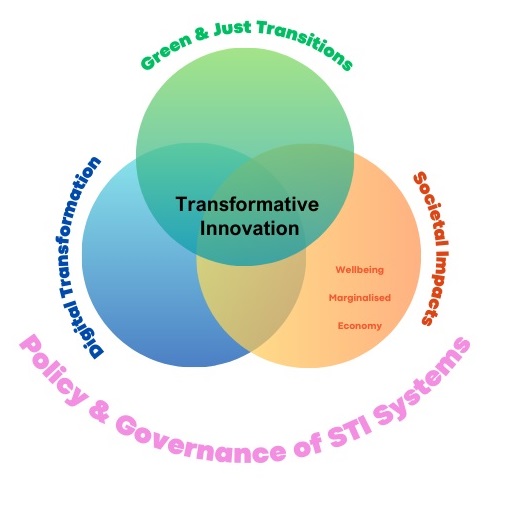
What is TIP and Why TIP Matters
Transformative Innovation Policy represents a paradigm shift in how innovation is understood and implemented. Unlike traditional innovation policies focused on economic growth and competitiveness, TIP emphasises systemic change, social inclusion, and sustainability. In Africa, and particularly South Africa, TIP is critical for addressing complex challenges such as climate change, inequality, and the localisation of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
TIP supports mission-oriented, systemic change, enabling government and stakeholders to steer innovation toward inclusive spatial transformation, sustainable building ecosystems, and improved quality of life for low-income households. By promoting experimentation (e.g. piloting new tenure models, alternative building technologies or community-led upgrading), co-creation with communities, and cross-sector collaboration, TIP helps shift the human settlements system onto a more equitable, climate-resilient and future-oriented trajectory. This makes TIP especially important for South Africa, where innovation must do more than create economic value, it must directly address social justice, spatial redress, and environmental sustainability. This approach ensures innovation addresses social justice, spatial redress, and environmental sustainability, fully aligning with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Key Principles of TIP
- Mission-Oriented Policy: Define clear societal missions (e.g., reducing housing backlog, promoting climate-resilient settlements).
- Systemic Change: Address root causes of spatial inequality and infrastructure deficits.
- Inclusive Governance: Foster collaboration across government spheres, private sector, and communities.
- Experimentation and Learning: Support pilots and adaptive policy frameworks.
- Sustainability and Resilience: Integrate nature-based solutions and green technologies.
Resource Library: Driving Innovation Towards SDGs
Here are essential resources for understanding and applying TIP in South Africa:
- Giving Direction to Innovation Policy
This policy brief emphasises the importance of setting a clear strategic direction for innovation policy. It argues that innovation should not only aim for incremental improvements but also address pressing societal challenges. The document highlights the need for frameworks that encourage experimentation, learning, and adaptability, ensuring that innovation contributes to long-term transformative change.
- Mapping New Approaches to Innovation Policy for Stronger Transformative Outcomes in Africa
This paper explores innovative methodologies tailored to African contexts. It stresses inclusive governance in policy design, the integration of local knowledge systems, and the value of regional collaboration for shared learning. By adopting these approaches, African countries can strengthen their capacity to achieve transformative outcomes that align with sustainable development goals.
- The Role of Transformative Innovation for SDGs Localisation: Insights from the South-African “Living Catchments Project”
The Living Catchments Project serves as a practical example of TIP in action. It demonstrates how water resource management can be integrated with community participation to achieve SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation). The case study underscores the importance of multi-stakeholder engagement, adaptive governance, and innovation in addressing complex environmental challenges.
- Towards a Transformative Innovation Policy (TIP) Research Agenda
This resource sets out a forward-looking research agenda for TIP. It calls for deeper understanding of socio-technical transitions, the development of indicators to measure transformative outcomes, and the role of experimentation in policy processes. These priorities aim to strengthen the evidence base for TIP and guide future policy development.
- Transformative Innovation for Sustainable Human Settlements: A South African Context
Focused on housing and urban development, this book highlights TIP as a tool for addressing spatial inequality and promoting sustainable human settlements. It discusses innovations in affordable housing, infrastructure, and urban planning, linking these efforts to climate resilience and inclusive growth strategies.
- Transformative Innovation Policy: Perspectives from South Africa 2021
This resource provides insights into South Africa’s progress in embedding TIP principles within its national policy framework. It identifies challenges such as policy coherence and institutional capacity while highlighting opportunities for integrating TIP into national development plans and sectoral strategies.
- Transformative Innovation Policy in Emerging Economies: What Does It Entail?
The paper examines TIP in the context of emerging economies, where balancing economic growth with sustainability is a key challenge. It discusses structural barriers to innovation and the need for inclusive innovation ecosystems that foster equitable development and social transformation.
- Transformative Innovation Policy: Lessons from the Innovation System Literature
Drawing on theoretical foundations, this resource emphasises systemic thinking in innovation policy. It explores the role of networks, institutions, and historical transitions in driving transformative change, offering lessons that can inform the design of future TIP frameworks.
- Transforming Science, Technology and Innovation Policies in Africa: Insights from Ghana, Kenya, Senegal, and South Africa
This comparative analysis examines STI policy transformations across four African countries. It identifies common challenges such as resource constraints and governance gaps, while highlighting success factors like strong leadership and regional cooperation. The paper concludes with recommendations for scaling transformative approaches across the continent.



Comments